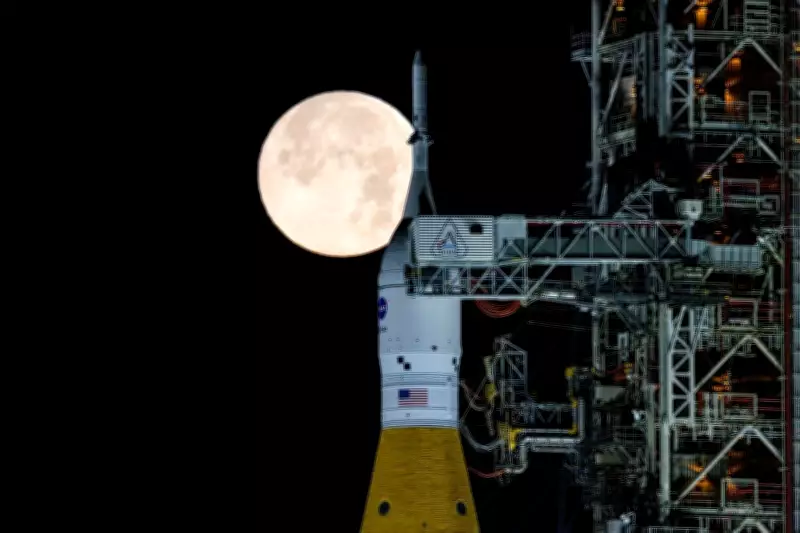
NASA Aims for March Launch of Artemis II Moon Rocket Following Fuel Leak Resolution
NASA has officially targeted a March launch window for its highly anticipated Artemis II mission, a critical step in returning humans to the lunar surface. This decision comes after engineers successfully addressed a fuel leak issue that was identified during recent testing procedures. The space agency remains focused on ensuring all systems are fully operational and safe for the crewed flight around the Moon.
Addressing Technical Challenges at Kennedy Space Center
The fuel leak was discovered during a comprehensive test run of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This testing phase is designed to simulate launch conditions and uncover any potential anomalies before the actual mission. NASA engineers have since conducted thorough investigations and implemented necessary repairs to mitigate the leak, allowing the agency to proceed with confidence toward a March launch timeline.
Artemis II represents a pivotal milestone in NASA's broader Artemis program, which aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon. This mission will carry a crew of astronauts on a journey around the Moon, testing the spacecraft's life support systems and navigation capabilities in deep space. The successful resolution of the fuel leak underscores NASA's commitment to rigorous safety protocols and meticulous preparation.
Preparations and Next Steps for the Lunar Mission
With the technical issue now resolved, NASA teams are advancing through the final stages of pre-launch preparations. Key activities include:
- Final integration checks of the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft
- Comprehensive reviews of all flight systems and crew safety measures
- Coordination with international partners contributing to the mission
The March launch target provides a strategic window that aligns with optimal orbital mechanics for the lunar trajectory. NASA will continue to monitor weather conditions and conduct additional tests as needed to ensure a successful liftoff. This mission not only advances lunar exploration but also sets the stage for future Artemis missions, including planned landings on the Moon's surface.