Saskatchewan Climate Group Files Appeal in Coal Power Legal Challenge
A climate advocacy organization based in Saskatchewan has formally filed an appeal in an ongoing legal challenge concerning the operation of a major coal-fired power plant in the province. The move represents a significant escalation in efforts to address environmental and regulatory concerns associated with fossil fuel infrastructure in the region.
Focus on Poplar River Power Plant
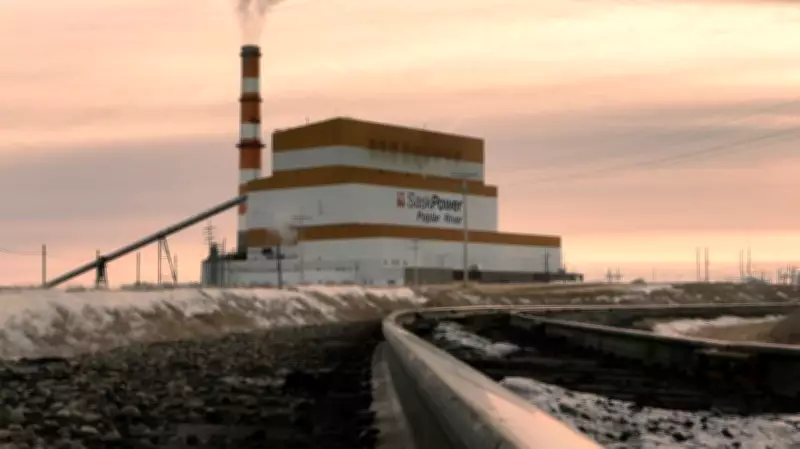
The legal action centers on SaskPower's Poplar River Power Plant, which is situated near the town of Coronach, Saskatchewan. This facility has been a point of contention for environmental groups due to its emissions and impact on local ecosystems. The appeal argues that previous rulings did not adequately consider the plant's long-term environmental consequences or compliance with evolving climate policies.
The climate group contends that the power plant's operations contribute substantially to greenhouse gas emissions, undermining provincial and national climate targets. They emphasize that transitioning away from coal is critical for meeting Canada's commitments under international climate agreements. The appeal documents likely highlight issues related to air quality, carbon pollution, and the sustainability of continued coal reliance in an era prioritizing renewable energy.
Broader Context and Implications
This legal appeal occurs against a backdrop of increasing scrutiny on coal power across Canada and globally. Saskatchewan, with its resource-based economy, faces unique challenges in balancing energy needs with environmental stewardship. The outcome of this case could set precedents for how similar facilities are regulated and potentially phased out in the future.
Environmental advocates argue that delaying the transition to cleaner energy sources poses risks to public health and the climate. They point to scientific studies linking coal emissions to respiratory illnesses and climate change effects, such as extreme weather events. The appeal may also address procedural aspects, such as whether regulatory approvals for the plant were granted with sufficient public consultation and environmental assessment.
Potential Outcomes and Next Steps
The appeal process will involve legal hearings where both sides present arguments before a higher court. Key factors under consideration may include:
- The plant's compliance with federal and provincial environmental regulations.
- The economic and social impacts of potentially restricting or closing the facility.
- Alternative energy solutions that could replace coal power in the region.
This case underscores the ongoing tension between traditional energy sectors and climate action in Canada. As legal proceedings advance, stakeholders from industry, government, and environmental groups will be closely monitoring developments. The appeal highlights a growing trend of using legal avenues to challenge fossil fuel projects, reflecting broader societal shifts toward sustainability and accountability in energy production.