Memory Chip Squeeze Widens Gap Between Market Winners and Losers
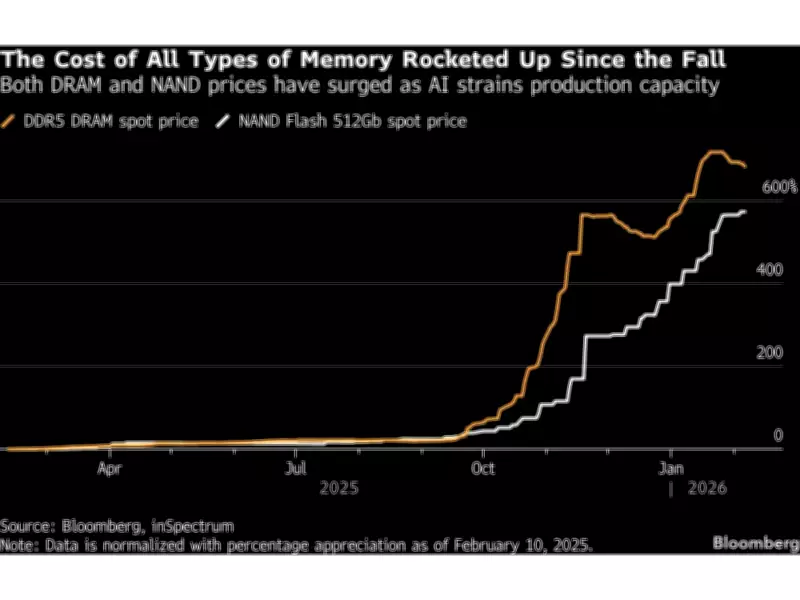
The relentless surge in memory chip prices over recent months has created a dramatic divide in global stock markets, with clear winners and losers emerging as investors assess the ongoing supply crisis. This situation shows no signs of immediate resolution, creating significant challenges across multiple technology sectors.
Market Performance Reveals Stark Contrast
A Bloomberg gauge tracking global consumer electronics manufacturers has declined approximately 10% since late September, reflecting growing investor concerns about profitability pressures. Meanwhile, a basket of memory chip producers including industry giant Samsung Electronics has experienced a remarkable surge of roughly 160% during the same period. This stark contrast highlights how the memory chip shortage is reshaping investment landscapes and corporate fortunes.
Companies ranging from game console manufacturer Nintendo to major PC brands and Apple suppliers are witnessing significant share price declines as profitability concerns mount. Memory producers, in contrast, are reaching unprecedented valuation heights as demand continues to outstrip available supply.
Corporate Strategies and Investor Concerns
Money managers and analysts are now carefully evaluating which companies can best navigate the current squeeze through various strategies including securing long-term supply contracts, implementing price increases on finished products, or redesigning products to utilize less memory. The question of how much of this supply disruption is already priced into current valuations remains a central concern for investors.
Vivian Pai, a fund manager at Fidelity International, noted that current market valuations largely assume the disruption will normalize within one to two quarters. However, she emphasized that industry tightness is likely to persist, potentially continuing through the remainder of the year. This duration risk may not be fully appreciated by current market pricing.
Specific Sector Impacts and Corporate Examples
Personal computer manufacturers are among the hardest hit by the memory chip squeeze. Both Lenovo Group and Dell Technologies have declined more than 25% from their respective peaks reached in October. Concerns that higher chip prices will dampen PC demand have also affected peripheral manufacturers like Swiss-based Logitech International, which has fallen nearly 30% from its November peak.
Elsewhere in the technology landscape, shares of Chinese electric vehicle and smartphone manufacturers including BYD and Xiaomi have shown sluggish performance amid worries related to chip shortages. The automotive sector is also feeling the pressure, with Honda Motor recently noting emerging supply risks for memory components during earnings discussions.
Earnings Season Revelations and Market Reactions
Memory chip shortages and pricing pressures have become frequent topics during recent earnings reports and conference calls across multiple industries. Charu Chanana, chief investment strategist at Saxo, observed that memory prices have moved from background conversations to headline concerns this earnings season. While the market broadly understands that memory prices are elevated and supply is constrained, the timeline of this supply tightness is now being questioned by investors.
Recent market reactions demonstrate the severity of the situation. Qualcomm shares fell more than 8% in a single trading session after the smartphone processor manufacturer signaled that memory constraints would limit phone production. Nintendo experienced its most significant decline in eighteen months following warnings about margin pressure resulting from chip shortages.
Broader Implications and Future Outlook
Concerns over demand and earnings are weighing heavily on the corporate landscape, with additional worries that massive artificial intelligence infrastructure spending by U.S. hyperscale cloud providers could further exacerbate memory chip shortages. The substantial build-out of AI infrastructure led by companies like Amazon has shifted production capacity toward high-bandwidth memory and away from traditional DRAM, creating additional supply chain complexities.
As the memory chip squeeze continues to reshape market dynamics, investors remain vigilant about which companies can successfully navigate these challenging conditions. The divide between winners and losers appears likely to widen further as supply constraints persist and corporate strategies are tested in this unprecedented semiconductor environment.